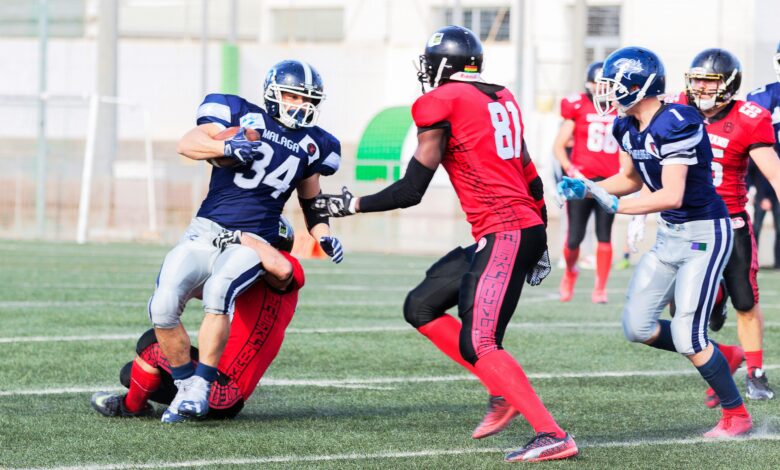
Cross-training refers to the practice of engaging in multiple types of physical activities to improve overall performance. Unlike focusing on a single sport or exercise, cross-training involves a variety of workouts that target different muscle groups and fitness components. For athletes, this approach can be incredibly beneficial as it helps in building a more well-rounded physique, prevents overuse injuries, and can even break the monotony of repetitive training.
For example, a runner might include swimming, cycling, or strength training in their regimen. This variety not only enhances cardiovascular endurance but also improves muscular strength and flexibility. Cross-training can be customized to fit the specific needs and goals of an athlete, making it a versatile option for all levels of fitness.
1. Physical Benefits of Cross-Training for Athletes
Improved Overall Fitness
One of the most significant advantages of cross-training is the enhancement of overall fitness. By incorporating different exercises, athletes can work on various aspects of their physical health, such as cardiovascular endurance, muscle strength, flexibility, and agility. This holistic approach can lead to better performance in their primary sport.
Injury Prevention
Overuse injuries are common among athletes who focus solely on one sport. For instance, runners often face issues like shin splints and knee problems due to repetitive stress. Cross-training allows athletes to use different muscle groups, giving overworked muscles a chance to recover and reducing the risk of injury.
Enhanced Recovery
Engaging in low-impact activities like swimming or yoga can aid in recovery by improving circulation and reducing muscle stiffness. These activities also provide a mental break, helping athletes to stay motivated and focused on their training regimen.
2. Mental Benefits of Cross-Training for Athletes
Breaks Monotony
Training for a single sport can become monotonous over time, leading to a lack of motivation. Cross-training introduces variety, keeping workouts fresh and exciting. This variety can make training more enjoyable, which is crucial for maintaining long-term commitment and consistency.
Mental Resilience
Participating in different types of physical activities can challenge athletes in new ways, building mental resilience. For example, a cyclist who takes up yoga may find the slow, controlled movements challenging but beneficial for mental focus and clarity. This mental adaptability can translate into better performance under pressure in their primary sport.
Stress Relief
Different types of exercise offer different forms of stress relief. For instance, aerobic exercises like running can release endorphins, while activities like yoga can promote relaxation and mindfulness. By incorporating various activities, athletes can better manage stress, leading to improved mental well-being.
3. How to Implement Cross-Training in Your Routine
Identify Your Goals
Before diving into cross-training, it’s essential for athletes to identify their specific goals. Are you looking to improve endurance, build strength, or enhance flexibility? Knowing your objectives will help you choose the most effective types of cross-training exercises.
Choose Complementary Activities
Select activities that complement your primary sport. For example, if you’re a swimmer, incorporating weight training can help build upper body strength, while yoga can improve flexibility. Runners might benefit from cycling to enhance leg strength without the impact stress on joints.
Schedule and Balance
It’s crucial to schedule cross-training sessions appropriately. While cross-training is beneficial, it shouldn’t replace sport-specific training entirely. A balanced approach involves incorporating cross-training a few times a week, depending on the intensity and frequency of your primary sport’s training sessions.
Listen to Your Body
Cross-training can be a great way to diversify your workouts, but it’s essential to listen to your body. Pay attention to any signs of overtraining or discomfort, and adjust your routine accordingly. Rest and recovery are just as crucial in a cross-training regimen as they are in any training program.
Conclusion
Cross-training offers a multitude of benefits for athletes, from improved overall fitness and injury prevention to enhanced mental resilience and stress relief. By incorporating a variety of exercises into their training regimen, athletes can become more well-rounded, versatile, and prepared for the demands of their sport. Whether you’re a seasoned competitor or a recreational enthusiast, cross-training can be an invaluable addition to your training routine, helping you achieve your athletic goals while keeping you healthy and motivated.